PYTHON程式語言的學習-列表的語法與列表函數
4種集合變數:
- List(列表)是一個有序且可變的集合。 允許重複成員。
- tuple(元組)是一個有序且不可更改的集合。 允許重複成員。
- set(集合)是一個無序、不可更改和無索引的集合。沒有重複的成員。
- dictionary(字典)是一個有序的集合和可變的。 沒有重複的成員。
在這個講次當中我們學習如何使用列表(list)。
列表是最常用的Python數據類型,它可以作為一個方括號內的逗號分隔值出現。
列表的數據項不需要具有相同的類型
創建一個列表,只要把逗號分隔的不同的數據項使用方括號括起來即可。如下所示:
list1 = ['physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000]
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
list3 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
15 Functions you should Know to Master Lists in Python
- sort(): Sorts the list in ascending order.
- type(list): It returns the class type of an object.
- append(): Adds one element to a list.
- extend(): Adds multiple elements to a list.
- index(): Returns the first appearance of a particular value.
- max(list): It returns an item from the list with a max value.
- min(list): It returns an item from the list with a min value.
- len(list): It gives the overall length of the list.
- clear(): Removes all the elements from the list.
- insert(): Adds a component at the required position.
- count(): Returns the number of elements with the required value.
- pop(): Removes the element at the required position.
- remove(): Removes the primary item with the desired value.
- reverse(): Reverses the order of the list.
- copy(): Returns a duplicate of the list.
掌握 Python 列表的 15 個函數
- sort(),sorted(list):按升序對列表進行排序。a.sort(); b=sorted(a)
- type(list):返回對象的類類型。type(a)
- append():將一個元素添加到列表中。a.append(10)
- extend():將另一列表的多個元素添加到指定的列表中。a.extend(b)
- index():返回特定值第一次出現的位置。a.index('A')
- max(list):它從列表中返回一個具有最大值的項目max(a)。
- min(list):它從列表中返回一個具有最小值的項目min(a)。
- len(list):給出列表的總長度。len(a)
- clear():從列表中刪除所有元素。a.clear()
- insert():在需要的位置添加一個元素。a.insert(3,'THU')
- count():返回具有指定的元素個數。a.count()
- pop():移除指定位置的元素。a.pop(3)
- remove():刪除具有所需值的主要項目。a.remove(4)
- reverse():反轉列表的順序。a.reverse()
- copy():返回列表的副本。
建立列表
學習重點:
- type(a):返回對象的類類型。
- a[5]:a 的第5元素。
- for i in a:迴圈與列表結合,迴圈變數i會走過a內的所有元素。
- if ... else ...:條件判斷的寫法,注意行末有冒號,區塊內的指令要退4格。
a=[1,2,3,6,7,8,9]
b=['A','B','C']
print(type(a[5]))
print('a=',a,' a[5]=',a[5])
for i in a:
for j in b:
print(i,j,end=' ')
print('')
for i in a:
if( i < 5):
print(i,b[0])
else:
print(i,b[2])
a= [1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9] a[5]= 8
1 A 1 B 1 C
2 A 2 B 2 C
3 A 3 B 3 C
6 A 6 B 6 C
7 A 7 B 7 C
8 A 8 B 8 C
9 A 9 B 9 C
1 A
2 A
3 A
6 C
7 C
8 C
9 C
列表中的列表(二維列表)
學習重點:
- a[0][1]:給出列表的[0][1]元素。
- 巢狀迴圈對應二維列表座標。
a=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
n=0
for i in a:
n+=1
print(n,i)
print('a[0][1]=',a[0][1])
print('a[1][2]=',a[1][2])
print('a[2][1]=',a[2][1])
for i in range(len(a)):
for j in range(len(a[0])):
print(i,j,a[i][j])
1 [1, 2, 3]
2 [4, 5, 6]
3 [7, 8, 9]
a[0][1]= 2
a[1][2]= 6
a[2][1]= 8
0 0 1
0 1 2
0 2 3
1 0 4
1 1 5
1 2 6
2 0 7
2 1 8
2 2 9
列表求和
學習重點:
- len(a),給出列表的總長度。
- sum(a),計算列表中這些數的總和。
a= [3.45, 3.13, 3.09, 2.78, 2.5, 0.33, 2.27, 1.91]
La=len(a)
print('len(a)=',La,' a=',a)
S=0
for i in a:
S+=i
print('S=',S)
S2=sum(a)
print('S2=',S2)
len(a)= 8 a= [3.45, 3.13, 3.09, 2.78, 2.5, 0.33, 2.27, 1.91]
S= 19.46
S2= 19.46
列表最大值與排序
學習重點:
- 列表中最大值:max(a)
- 列表中最小值:min(a)
- append():將一個元素添加到列表中。a.append(x)
- remove():刪除具有所需值的主要項目。a.remove(x)
- reverse():反轉列表的順序。a.reverse()
- b2=sorted(a3):按升序對列表進行排序。
- copy():返回列表的副本。
a= [3.09, 3.45, 0.33, 3.13, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
print('a1=',a)
a2=a
a3=a.copy()
La=len(a)
print(max(a))
print(min(a))
b=[]
for i in range(La):
x=max(a)
b.append(x)
a.remove(x)
print(x,a)
print('b1=',b)
print('a2=',a2)
print('a3=',a3)
b2=sorted(a3)
print('b2=',b2)
b3=b2.copy()
b3.reverse()
print('b3=',b3)
a1= [3.09, 3.45, 0.33, 3.13, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
3.45
0.33
3.45 [3.09, 0.33, 3.13, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
3.13 [3.09, 0.33, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
3.09 [0.33, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
2.78 [0.33, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
2.5 [0.33, 2.27, 1.91]
2.27 [0.33, 1.91]
1.91 [0.33]
0.33 []
b1= [3.45, 3.13, 3.09, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91, 0.33]
a2= []
a3= [3.09, 3.45, 0.33, 3.13, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91]
b2= [0.33, 1.91, 2.27, 2.5, 2.78, 3.09, 3.13, 3.45]
b3= [3.45, 3.13, 3.09, 2.78, 2.5, 2.27, 1.91, 0.33]
列表元素合併與插入
學習重點:
- a.extend(b):將另一列表的多個元素添加到指定的列表中。
- a.insert(3,"Tunghai"):在指定的位置添加一個元素。。
a=[1,2,3]; b=['A','B','C']
print('\n\nb=',b)
print('before extend(b): a=',a)
a.extend(b)
print('after a.extend(b), a=',a)
a.insert(3,"Tunghai")
print('a.insert(3,"Tunghai"): a=',a)
b= ['A', 'B', 'C']
before extend(b): a= [1, 2, 3]
after a.extend(b), a= [1, 2, 3, 'A', 'B', 'C']
a.insert(3,"Tunghai"): a= [1, 2, 3, 'Tunghai', 'A', 'B', 'C']
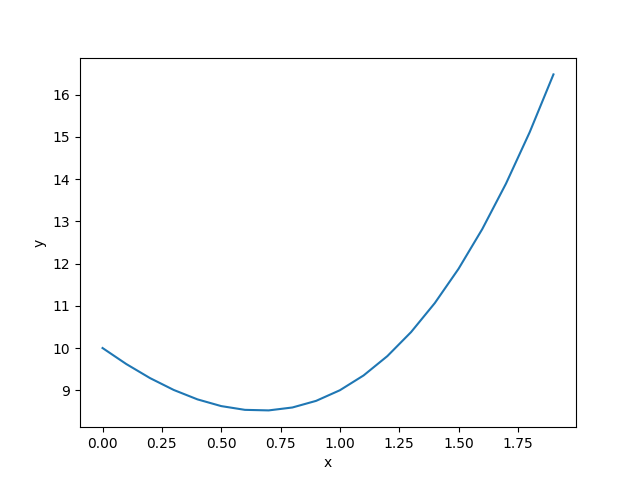
列表應用於積分與畫圖
學習重點:
- 精確積分計算:
我們可以利用列表來進行積分的運算。
同學們只要知道多項式如何微分,就知道一個多項式積分該如何進行,因為微分和積分互為逆運算:
\[\frac{d}{dx} [a x^n]=nax^{n-1} \Rightarrow \int a x^n \, dx=\dfrac{a}{n+1} x^{n+1} \]
\[\int_0^2 x^3+2x^2-4x+10 \, dx=\left[ \frac{1}{4} x^4 +\frac{2}{3} x^3 -2 x^2 + 10x \right]_0^2\]
- 數值積分計算
- 在給定的區間(a,b)分割N個等間隔,每一個間隔的寬度dx=(b-a)/N。
對每一個間隔計算所對應的y坐標,也就是這個區間代表性的x對應的函數值。
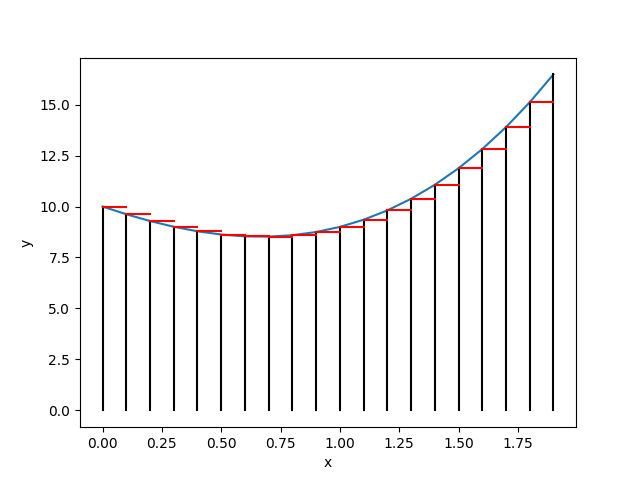
- 將區間所對應到的矩形面積算出,再把所有區間的面積求和,就可得到這個函數在(a,b)中的積分。
- 在迴圈中陸續產生的x坐標和y坐標都分別收錄至Lx和Ly的列表當中。
最後利用matplotlib繪圖模組,將兩個列表Lx,Ly中的數據,繪製成圖形。
- 最後一步,為了顯現出我們的等間隔分割所對應的矩形,我們又再度利用迴圈畫出垂直的矩形邊長。
N=20; a=0; b=2; dx=(b-a)/N
Lx=[]; Ly=[]; I=[]
for i in range(N):
x=a+dx*i
y=x**3+2*x**2-4*x+10
Lx.append(x)
Ly.append(y)
I.append(dx*y)
print(sum(I))
x=b
A2=x**4/4+2*x**3/3-2*x**2+10*x
x=a
A1=x**4/4+2*x**3/3-2*x**2+10*x
print(A2-A1)
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matplotlib.use("Agg")
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.plot(Lx,Ly)
plt.savefig("FIG-1.png")
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.plot(Lx,Ly)
for i in range(N):
plt.plot([Lx[i],Lx[i]],[0,Ly[i]],'k-')
for i in range(N-1):
plt.plot([Lx[i],Lx[i+1]],[Ly[i],Ly[i]],'r-')
plt.savefig("FIG-2.png")
print ('plot is done')
20.95
21.333333333333332
plot is done